Magnetometro GY-273 QMC5883L clone HMC5883L per Arduino, esp8266 e esp32

Un magnetometro è un dispositivo che misura il campo magnetico o il momento del dipolo magnetico. Alcuni magnetometri misurano la direzione, la forza o il cambiamento relativo di un campo magnetico in una posizione particolare.
Ad esempio, una bussola è un semplice magnetometro

Con questo principio, un dispositivo può capire se ha cambiato posizione o direzione sui 3 assi x, y e z.
Ho comprato questo sensore (e altri dello stesso tipo) per i miei progetti, e ho scoperto che non è così semplice da usare.
Primo, perché molti di questi non sono un HMC5883L ma un QMC5883L e la libreria e l’indirizzo non sono gli stessi.
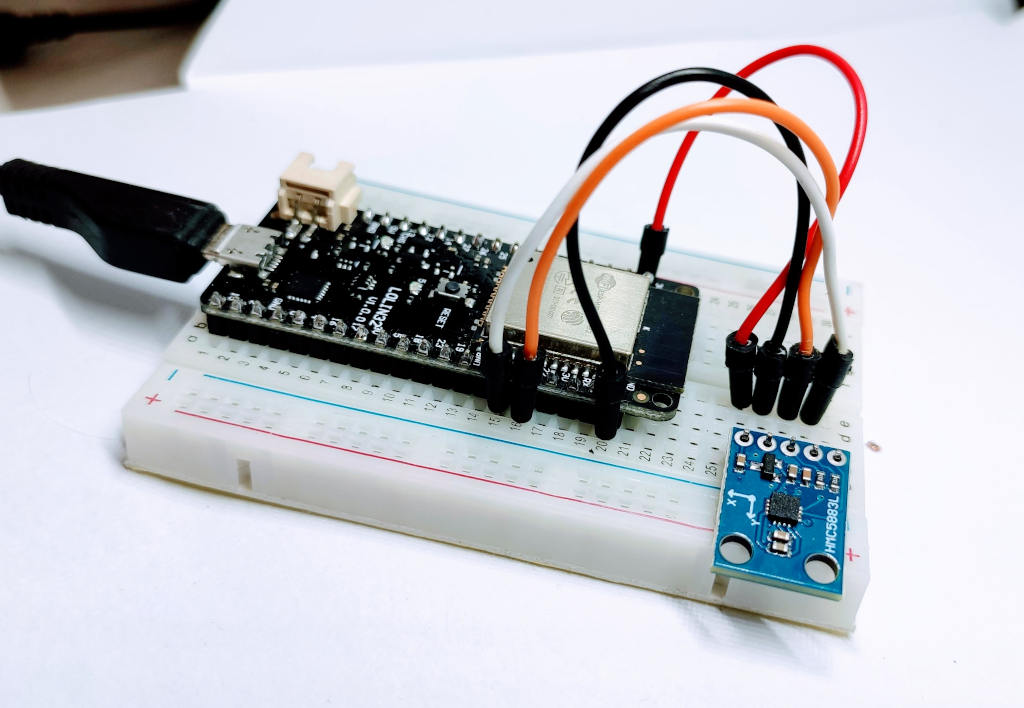
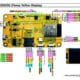
Cablaggio
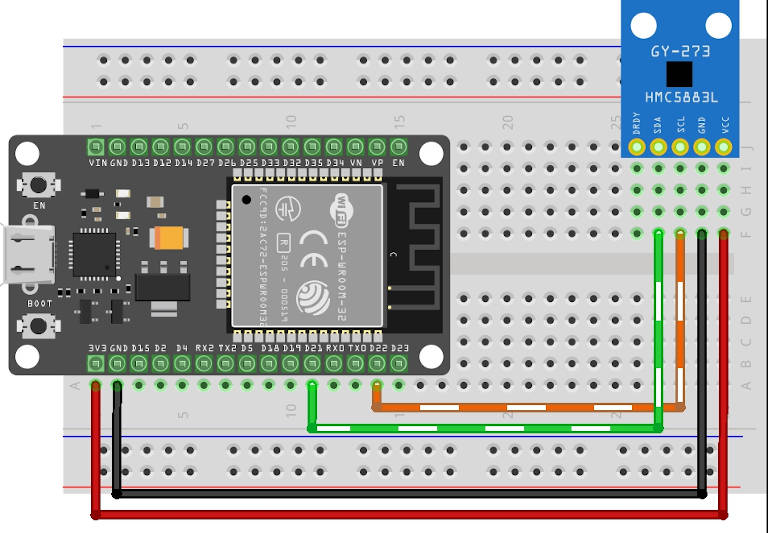
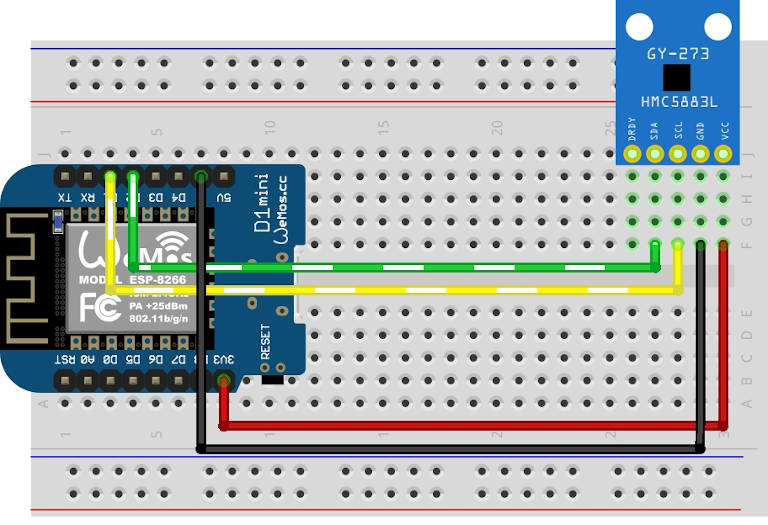
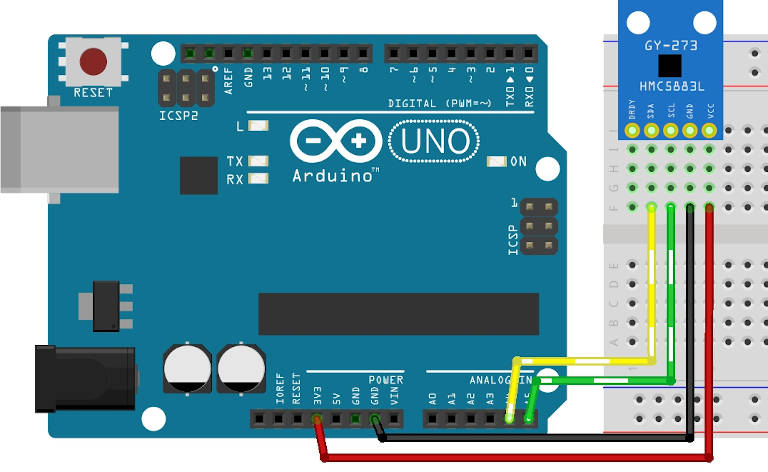
Ecco alcuni semplici esempi di cablaggio.
esp32:
esp8266, WeMos D1 mini:
Arduino UNO:
Inizia la prototipazione
Verifica variante
Il modo semplice per identificare se si tratta di una variante QMC5883L è utilizzare uno scanner i2c. La variante aveva un indirizzo (0x0D) diverso da quello originale HMC5883L.
/*
* i2c scanner
* Renzo Mischianti www.mischianti.org
*/
#include <Wire.h>
void setup() {
Wire.begin();
Serial.begin(115200);
while (!Serial) {delay(100);};
Serial.println();
Serial.println("I2C Scanner");
}
void loop() {
byte error, address;
int nDevices;
Serial.println("Scanning...");
nDevices = 0;
for(address = 1; address < 127; address++ ) {
Wire.beginTransmission(address);
error = Wire.endTransmission();
if (error == 0) {
Serial.print("I2C device found at address 0x");
if (address<16) {
Serial.print("0");
}
Serial.println(address,HEX);
nDevices++;
}
else if (error==4) {
Serial.print("Unknow error at address 0x");
if (address<16) {
Serial.print("0");
}
Serial.println(address,HEX);
}
}
if (nDevices == 0) {
Serial.println("No I2C devices found\n");
}
else {
Serial.println("done\n");
}
delay(5000);
}
se si ottiene questo output, si ha una variante QMC5883L
Scanning...
I2C device found at address 0x0D
done
Scanning...
I2C device found at address 0x0D
done
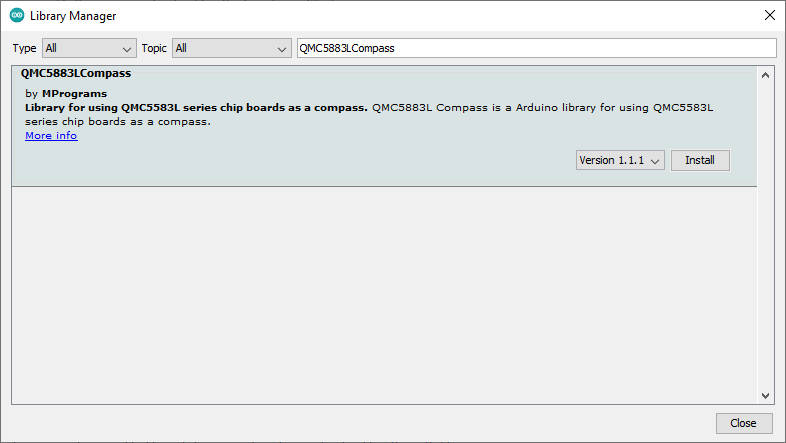
Library
Uso la libreria QMC5883LCompass che puoi trovare su GitHub, oppure puoi scaricare direttamente dall’Arduino Libray manager.
Codice
Ecco un piccolo codice che ho scritto prendendone parti da qualche esempio e aggiungo la stampa delle coordinate calcolate dall’azimut.
Quindi nel codice, prima, chiede di calibrare il dispositivo e dopo la calibrazione, inizia a emettere i valori.
/*
* Simple sketch that use
* QMC5883LCompass.h from https://github.com/mprograms/QMC5883LCompass
* library.
* First the sketch ask to calibrate device so move It, then
* start to output the data
*
* by Mischianti Renzo <https://mischianti.org>
*
* https://mischianti.org
*
*/
#include <QMC5883LCompass.h>
QMC5883LCompass compass;
int calibrationData[3][2];
bool changed = false;
bool done = false;
int t = 0;
int c = 0;
bool calibrated = false;
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600);
// Initialize device with i2c 0x0D address
compass.init();
}
void loop() {
if (!calibrated){
// If not calibrated
int x, y, z;
// Read compass values
compass.read();
// Return XYZ readings
x = compass.getX();
y = compass.getY();
z = compass.getZ();
changed = false;
if(x < calibrationData[0][0]) {
calibrationData[0][0] = x;
changed = true;
}
if(x > calibrationData[0][1]) {
calibrationData[0][1] = x;
changed = true;
}
if(y < calibrationData[1][0]) {
calibrationData[1][0] = y;
changed = true;
}
if(y > calibrationData[1][1]) {
calibrationData[1][1] = y;
changed = true;
}
if(z < calibrationData[2][0]) {
calibrationData[2][0] = z;
changed = true;
}
if(z > calibrationData[2][1]) {
calibrationData[2][1] = z;
changed = true;
}
if (changed && !done) {
Serial.println("CALIBRATING... Keep moving your sensor around.");
c = millis();
}
t = millis();
if ( (t - c > 5000) && !done) {
done = true;
Serial.println("DONE.");
Serial.println();
Serial.print("compass.setCalibration(");
Serial.print(calibrationData[0][0]);
Serial.print(", ");
Serial.print(calibrationData[0][1]);
Serial.print(", ");
Serial.print(calibrationData[1][0]);
Serial.print(", ");
Serial.print(calibrationData[1][1]);
Serial.print(", ");
Serial.print(calibrationData[2][0]);
Serial.print(", ");
Serial.print(calibrationData[2][1]);
Serial.println(");");
compass.setCalibration( calibrationData[0][0], calibrationData[0][1], calibrationData[1][0],
calibrationData[1][1], calibrationData[2][0], calibrationData[2][1]);
calibrated = true;
}
}else{
// If calibrating
int x, y, z;
// Read compass values
compass.read();
// Return XYZ readings
x = compass.getX();
y = compass.getY();
z = compass.getZ();
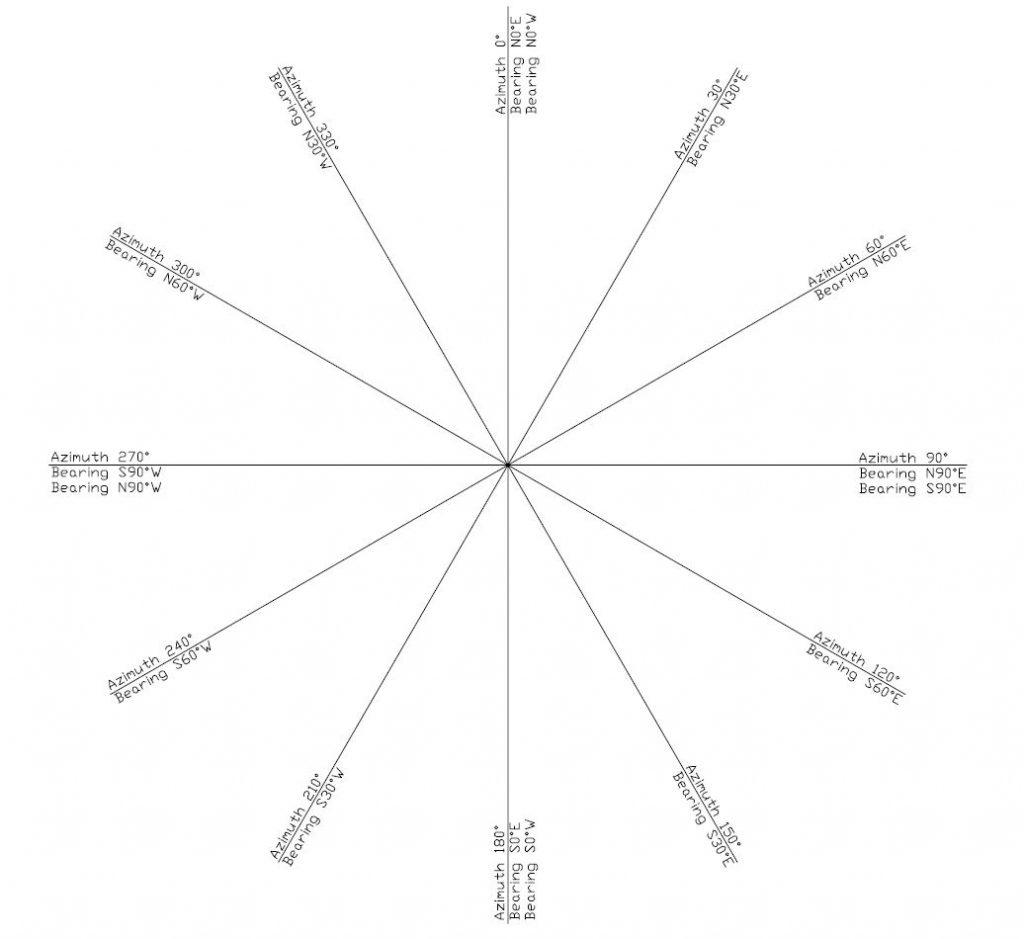
int azimut = compass.getAzimuth();
float bearing = compass.getBearing(azimut);
Serial.println();
// Write direction
if((azimut < 22.5) || (azimut > 337.5 )) Serial.print("North ");
if((azimut > 22.5) && (azimut < 67.5 )) Serial.print("North-East");
if((azimut > 67.5) && (azimut < 112.5 )) Serial.print("East ");
if((azimut > 112.5) && (azimut < 157.5 )) Serial.print("South-East");
if((azimut > 157.5) && (azimut < 202.5 )) Serial.print("South ");
if((azimut > 202.5) && (azimut < 247.5 )) Serial.print("SOuth-West");
if((azimut > 247.5) && (azimut < 292.5 )) Serial.print("West ");
if((azimut > 292.5) && (azimut < 337.5 )) Serial.print("North-West");
Serial.print(" Azimuth: ");Serial.print(azimut);
Serial.print(" Bearing: ");Serial.print(bearing);
Serial.print(" - X: ");
Serial.print(x);
Serial.print(" Y: ");
Serial.print(y);
Serial.print(" Z: ");
Serial.print(z);
delay(250);
}
}
Ecco il risultato dell’output seriale
CALIBRATING... Keep moving your sensor around.
[...]
CALIBRATING... Keep moving your sensor around.
DONE. Copy the line below and paste it into your projects sketch.);
compass.setCalibration(0, 1372, -1106, 0, 0, 966);
North-West Azimuth: 321 Bearing: 14.00 - X: 1130 Y: -948 Z: 492
North-West Azimuth: 320 Bearing: 14.00 - X: 1035 Y: -881 Z: 432
North-West Azimuth: 320 Bearing: 14.00 - X: 941 Y: -814 Z: 374
North-West Azimuth: 319 Bearing: 14.00 - X: 845 Y: -747 Z: 316
North-West Azimuth: 318 Bearing: 14.00 - X: 752 Y: -681 Z: 257
North-West Azimuth: 317 Bearing: 14.00 - X: 656 Y: -614 Z: 197
North-West Azimuth: 316 Bearing: 14.00 - X: 561 Y: -550 Z: 138
North-West Azimuth: 314 Bearing: 13.00 - X: 466 Y: -483 Z: 80
North-West Azimuth: 312 Bearing: 13.00 - X: 372 Y: -417 Z: 22
North-West Azimuth: 312 Bearing: 13.00 - X: 372 Y: -416 Z: 21
North-West Azimuth: 312 Bearing: 13.00 - X: 373 Y: -416 Z: 22
North-West Azimuth: 314 Bearing: 13.00 - X: 383 Y: -399 Z: 24
North-West Azimuth: 319 Bearing: 14.00 - X: 383 Y: -335 Z: 60
North-West Azimuth: 326 Bearing: 14.00 - X: 369 Y: -257 Z: 107
North-West Azimuth: 333 Bearing: 14.00 - X: 348 Y: -179 Z: 165
North Azimuth: 346 Bearing: 15.00 - X: 328 Y: -83 Z: 227
North Azimuth: 4 Bearing: 0.00 - X: 307 Y: 25 Z: 292
North-East Azimuth: 26 Bearing: 1.00 - X: 289 Y: 142 Z: 356
North-East Azimuth: 43 Bearing: 1.00 - X: 272 Y: 260 Z: 420
North-East Azimuth: 55 Bearing: 2.00 - X: 253 Y: 363 Z: 484
North-East Azimuth: 61 Bearing: 2.00 - X: 226 Y: 418 Z: 513
North-East Azimuth: 63 Bearing: 2.00 - X: 223 Y: 447 Z: 515
North-East Azimuth: 63 Bearing: 2.00 - X: 230 Y: 458 Z: 515
North-East Azimuth: 63 Bearing: 2.00 - X: 230 Y: 458 Z: 514
North-East Azimuth: 59 Bearing: 2.00 - X: 247 Y: 425 Z: 496
North-East Azimuth: 53 Bearing: 2.00 - X: 246 Y: 328 Z: 444
North-East Azimuth: 40 Bearing: 1.00 - X: 246 Y: 208 Z: 391
North Azimuth: 18 Bearing: 0.00 - X: 245 Y: 83 Z: 326
North Azimuth: 354 Bearing: 15.00 - X: 259 Y: -31 Z: 264
North-West Azimuth: 332 Bearing: 14.00 - X: 277 Y: -148 Z: 202
North-West Azimuth: 320 Bearing: 14.00 - X: 294 Y: -252 Z: 144
North-West Azimuth: 313 Bearing: 13.00 - X: 312 Y: -338 Z: 99