BNO055 per esp32, esp8266 e Arduino: abilitare il pin INT e High G Interrupt dell’accelerometro – 5
Il BNO055 è un versatile sensore a 9 assi che combina un accelerometro, un giroscopio e un magnetometro per fornire un tracciamento dell’orientamento preciso in un pacchetto compatto. Dispone di un microcontrollore integrato e di algoritmi di fusione dei sensori avanzati che forniscono misurazioni stabili ed accurate anche in ambienti difficili.
Il BNO055 può essere utilizzato con una varietà di piattaforme di microcontrollore, tra cui esp32, esp8266 e Arduino. Per aiutare gli utenti ad iniziare con il BNO055, è stata creata una serie di articoli che coprono vari aspetti del lavoro con il modulo sensore.
Nella parte 1 della serie viene introdotta la libreria di base di Adafruit per l’uso con il BNO055. La parte 2 si concentra sulla connessione e sull’utilizzo della libreria avanzata di Bosch. La parte 3 copre le funzionalità, la configurazione e la riassegnazione degli assi, mentre la parte 4 si occupa delle modalità di alimentazione e della configurazione dell’interruzione di movimento qualsiasi o nessun movimento dell’accelerometro.
La parte 5, che è il focus di questa estratto, si concentra sull’abilitazione del pin INT e sulla configurazione dell’interruzione di accelerazione ad alta G. La parte 6 si occupa della configurazione dell’interruzione di alta velocità del giroscopio e di qualsiasi movimento.
Complessivamente, la serie di articoli fornisce una guida completa per lavorare con il BNO055 e sfruttare appieno il suo potenziale per una vasta gamma di applicazioni.
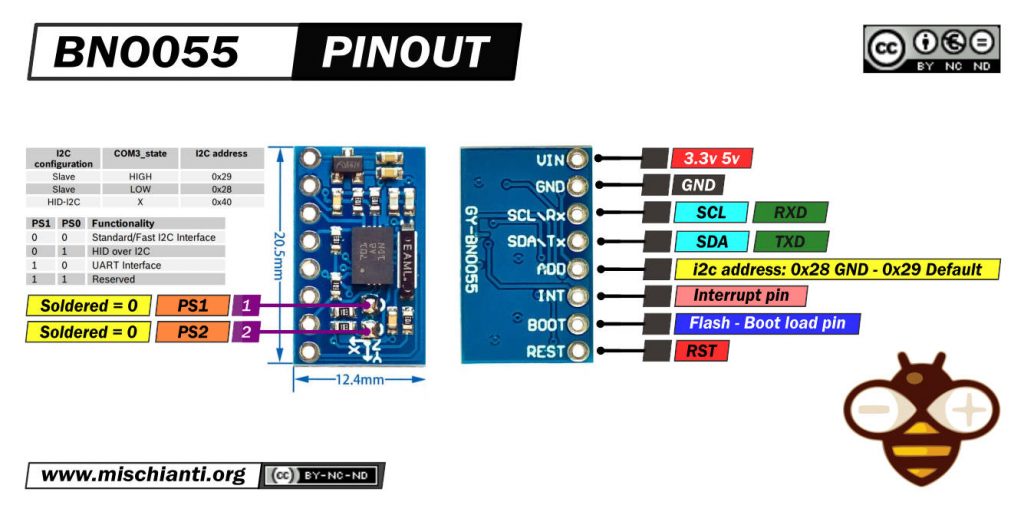
Piedinatura BNO055
Esistono molte versioni di moduli di questi sensori, quindi scelgo il più piccolo ed economico.
Ecco dove acquistare il modulo Aliexpress
Tutti questi moduli hanno le stesse funzionalità, ma per abilitarle è necessario eseguire operazioni diverse.
Questo è il clone che uso:
Ed ecco quello di Adafruit:
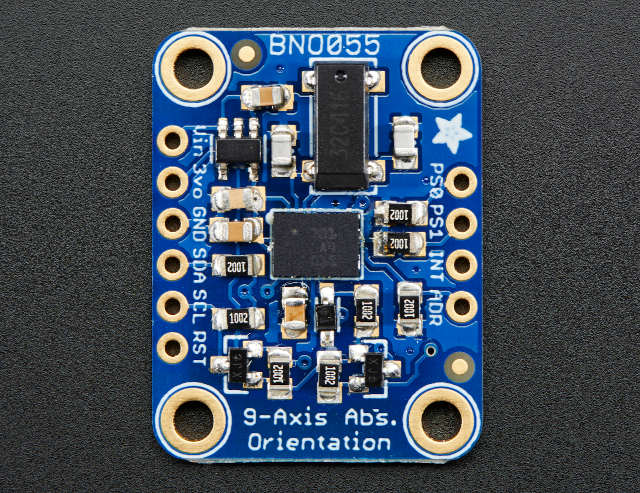
Il sensore supporta un livello logico 3.3v, ma il modulo può essere alimentato a 5v.
Interrupt del microcontrollore sul PIN
Ora, se vogliamo utilizzare il pin INT, aggiungeremo una maschera di bit e collegheremo un pin diinterrupt.
esp32 gestione degli interrupt
Per prima cosa, dobbiamo cablare il pin INT, è meglio selezionare un pin RTC (selezionare “ESP32 risparmio energetico pratico: preservare lo stato dei gpio, risveglio esterno e ULP“).
Ecco qui alcuni esp32 ESP32 Dev Kit v1 - TTGO T-Display 1.14 ESP32 - NodeMCU V3 V2 ESP8266 Lolin32 - NodeMCU ESP-32S - WeMos Lolin32 - WeMos Lolin32 mini - ESP32-CAM programmer - ESP32-CAM bundle - ESP32-WROOM-32 - ESP32-S - ESP32-WROOM-32 - ESP32 2.8 Inch Touch ESP32-2432S028
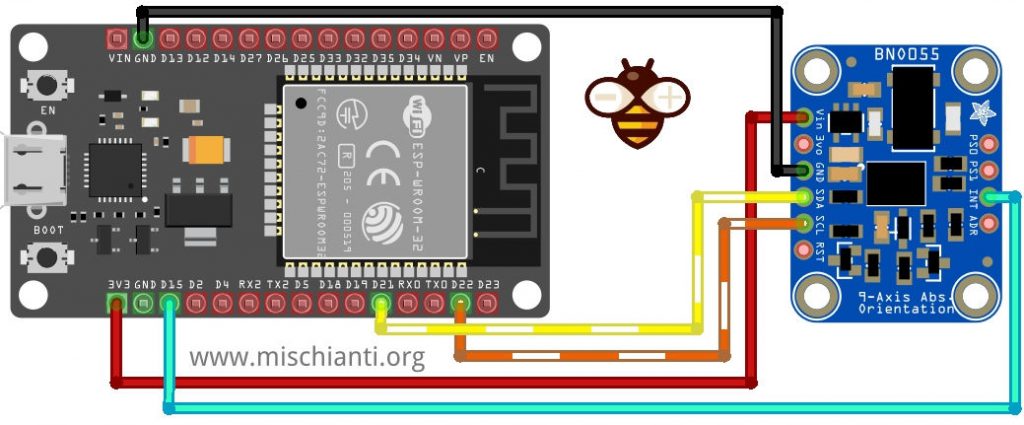
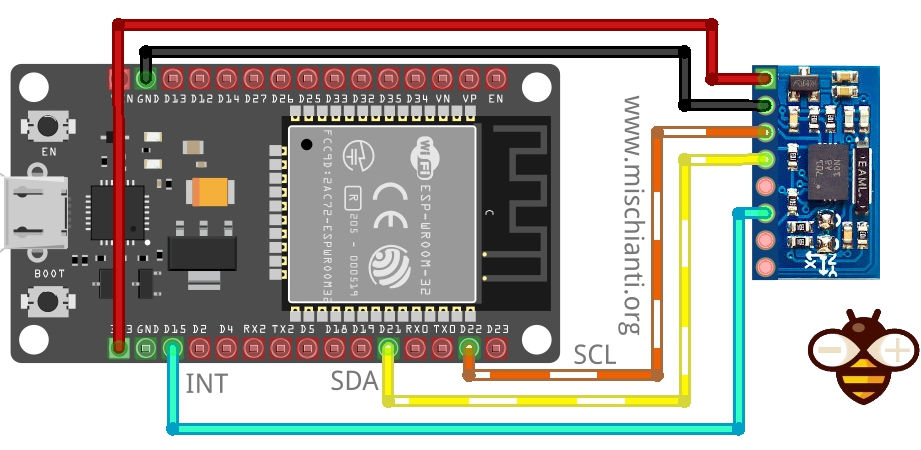
Il pin INT, è impostato HIGH all’interrupt e rimarrà HIGHo fino a quando non verrà resettato o letto dall’host, quindi su esp32, dobbiamo attaccare l’interrupt in questo modo:
bool somethingHappened = false;
void IRAM_ATTR interruptCallback() {
somethingHappened = true;
}
[...]
pinMode(INTERRUPT_PIN, INPUT);
attachInterrupt(INTERRUPT_PIN, interruptCallback, RISING);
Gestione degli interrupt Arduino
Le schede Arduino hanno dei pin che possono essere usati come interrupt,
| Schede | PIN DIGITALI UTILIZZABILI PER INTERRUPT |
|---|---|
| Uno, Nano, Mini, altri basati su 328 | 2, 3 |
| Uno WiFi Rev.2, Nano Every | tutti i pin digitali |
| Mega, Mega2560, MegaADK | 2, 3, 18, 19, 20, 21 |
| Micro, Leonardo, altri basati su 32u4 | 0, 1, 2, 3, 7 |
| Zero | all digital pins, except 4 |
| Schede della famiglia MKR | 0, 1, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, A1, A2 |
| Nano 33 IoT | 2, 3, 9, 10, 11, 13, A1, A5, A7 |
| Nano 33 BLE, Nano 33 BLE Sense | tutti i pins |
| Due | tutti i pins digitali |
| 101 | tutti i pins digitali (Solo i pins 2, 5, 7, 8, 10, 11, 12, 13 funzionano con CHANGE) |
per Arduino UNO, selezioneremo il pin 2,
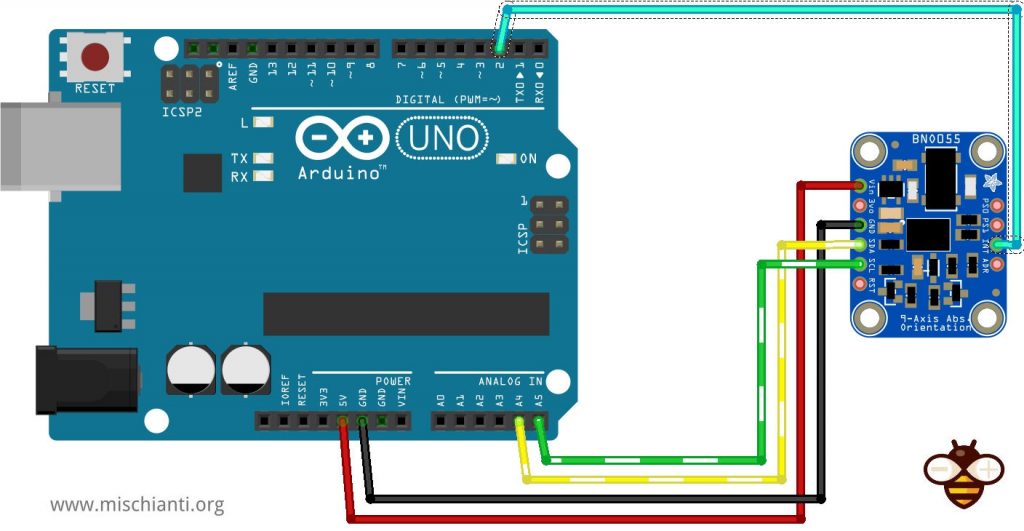
E dobbiamo gestire il pin di interrupt con lo stesso comportamento dell’esp32 già descritto.
pinMode(INTERRUPT_PIN, INPUT);
attachInterrupt(digitalPinToInterrupt(INTERRUPT_PIN), interruptCallback, RISING);
Gestione interrupt esp8266
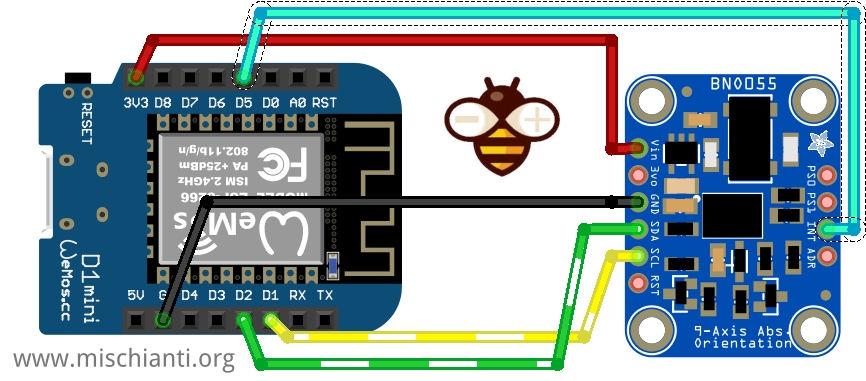
esp8266 come esp32 ha molti pin di interrupt e anche la gestione è simile. Ecco lo schema di cablaggio per il sensore Adafruit.
Ecco lo schema di cablaggio per clone bno055.
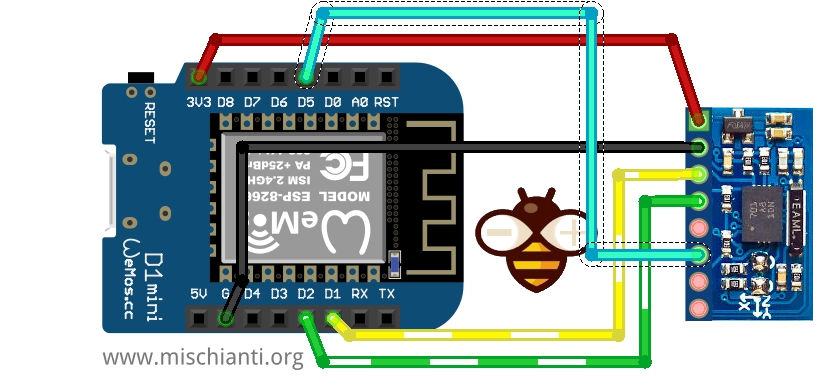
L’interrupt ha la stessa gestione dell’esp32, e selezioneremo il pin D5.
bool somethingHappened = false;
void IRAM_ATTR interruptCallback() {
somethingHappened = true;
}
[...]
pinMode(INTERRUPT_PIN, INPUT);
attachInterrupt(INTERRUPT_PIN, interruptCallback, RISING);
BitMask di interrupt
Per abilitare il pin INT, è necessario configurare la maschera di bit di interrupt.

Per attivare il pin di interrupt, dobbiamo impostare 1 alla maschera di bit di interrupt.
// Activate INT pin with bitmask
bno055_set_intmsk_accel_nomotion(1);
bno055_set_intmsk_accel_anymotion(1);
E ogni volta che abbiamo un interrupt per riattivare la gestione dei pin, dobbiamo impostare a 1 il registro RST_INT con questo comando.
// reset all previous int signal
bno055_set_reset_int(1);
Se non esegui questa operazione, il pin int rimane ALTO e puoi rilevare più interruzioni.
Ecco lo sketch completo.
/**
* bno055 simple interrupt management
* enable register interrupt and pin 15
* for any motion and no motion in LOW POWER mode
* bit mask for interrupt pin on no and any motion
*
* by Renzo Mischianti <www.mischianti.org>
*
* https://mischianti.org/
*/
#include "BNO055_support.h" //Contains the bridge code between the API and Arduino
#include <Wire.h>
//The device address is set to BNO055_I2C_ADDR2 in this example. You can change this in the BNO055.h file in the code segment shown below.
// /* bno055 I2C Address */
// #define BNO055_I2C_ADDR1 0x28
// #define BNO055_I2C_ADDR2 0x29
// #define BNO055_I2C_ADDR BNO055_I2C_ADDR2
//Pin assignments as tested on the Arduino Due.
//Vdd,Vddio : 3.3V
//GND : GND
//SDA/SCL : SDA/SCL
//PSO/PS1 : GND/GND (I2C mode)
//This structure contains the details of the BNO055 device that is connected. (Updated after initialization)
struct bno055_t myBNO;
struct bno055_euler myEulerData; //Structure to hold the Euler data
unsigned long lastTime = 0;
/* Set the delay between fresh samples */
#define BNO055_SAMPLERATE_DELAY_MS (1000)
#define INTERRUPT_PIN 15
void getIntInterruptEnabled();
void getIntInterruptBitMaskEnabled();
void getInterruptStatusEnabled(bool synthetic = false);
void printSlowMotionNoMotionParameters();
bool somethingHappened = false;
void IRAM_ATTR interruptCallback() {
somethingHappened = true;
}
void setup() //This code is executed once
{
//Initialize I2C communication
Wire.begin();
//Initialization of the BNO055
BNO_Init(&myBNO); //Assigning the structure to hold information about the device
// bno055_set_reset_sys(1);
delay(1500);
bno055_set_powermode(POWER_MODE_LOW_POWER);
// Activate INT pin with bitmask
bno055_set_intmsk_accel_nomotion(1);
bno055_set_intmsk_accel_anymotion(1);
// reset all previous int signal
bno055_set_reset_int(1);
//Configuration to NDoF mode
bno055_set_operation_mode(OPERATION_MODE_NDOF);
// Activate SLOW MOTION
// bno055_set_accel_slow_no_motion_enable(0);
// Activate NO MOTION (default)
bno055_set_accel_slow_no_motion_enable(1);
delay(1);
//Initialize the Serial Port to view information on the Serial Monitor
Serial.begin(115200);
pinMode(INTERRUPT_PIN, INPUT);
attachInterrupt(INTERRUPT_PIN, interruptCallback, RISING);
delay(1000);
getIntInterruptEnabled();
getIntInterruptBitMaskEnabled();
printSlowMotionNoMotionParameters();
}
bool suspended = false;
bool reactivated = false;
void loop() //This code is looped forever
{
if ((millis() - lastTime) >= BNO055_SAMPLERATE_DELAY_MS) //To stream at 10Hz without using additional timers
{
lastTime = millis();
bno055_read_euler_hrp(&myEulerData); //Update Euler data into the structure
Serial.print(millis()/1000); Serial.print("Secs - ");
/* The WebSerial 3D Model Viewer expects data as heading, pitch, roll */
Serial.print(F("Orientation: "));
Serial.print(360-(float(myEulerData.h) / 16.00));
Serial.print(F(", "));
Serial.print(360-(float(myEulerData.p) / 16.00));
Serial.print(F(", "));
Serial.print(360-(float(myEulerData.r) / 16.00));
Serial.print(F(" - "));
getInterruptStatusEnabled(true);
}
if (somethingHappened) {
Serial.println("---------------");
getInterruptStatusEnabled();
Serial.println("---------------");
bno055_set_reset_int(1);
somethingHappened = false;
}
}
/*
* Print the interrupt enabled
*/
void getIntInterruptEnabled() {
unsigned char gyro_am = 0;
unsigned char gyro_hr = 0;
unsigned char accel_hg = 0;
unsigned char accel_am = 0;
unsigned char accel_nm = 0;
bno055_get_int_gyro_anymotion(&gyro_am);
bno055_get_int_gyro_highrate(&gyro_hr);
bno055_get_int_accel_high_g(&accel_hg);
bno055_get_int_accel_anymotion(&accel_am);
bno055_get_int_accel_nomotion(&accel_nm);
Serial.println( "---- Interrupt enabled ----" );
Serial.print( "Gyro Any Motion " );
Serial.println( gyro_am );
Serial.print( "Gyro High Rate " );
Serial.println( gyro_hr );
Serial.print( "Accel High G " );
Serial.println( accel_hg );
Serial.print( "Accel Any Motion " );
Serial.println( accel_am );
Serial.print( "Accel No Motion " );
Serial.println( accel_nm );
Serial.println( "---------------------------" );
}
/*
* Print the interrupt to send on interrupt pin
*/
void getIntInterruptBitMaskEnabled() {
unsigned char gyro_am = 0;
unsigned char gyro_hr = 0;
unsigned char accel_hg = 0;
unsigned char accel_am = 0;
unsigned char accel_nm = 0;
bno055_get_intmsk_gyro_anymotion(&gyro_am);
bno055_get_intmsk_gyro_highrate(&gyro_hr);
bno055_get_intmsk_accel_high_g(&accel_hg);
bno055_get_intmsk_accel_anymotion(&accel_am);
bno055_get_intmsk_accel_nomotion(&accel_nm);
Serial.println( "---- Interrupt bitmask ----" );
Serial.print( "Gyro Any Motion " );
Serial.println( gyro_am );
Serial.print( "Gyro High Rate " );
Serial.println( gyro_hr );
Serial.print( "Accel High G " );
Serial.println( accel_hg );
Serial.print( "Accel Any Motion " );
Serial.println( accel_am );
Serial.print( "Accel No Motion " );
Serial.println( accel_nm );
Serial.println( "---------------------------" );
}
/*
* Print the interrupt status
*/
void getInterruptStatusEnabled(bool synthetic) {
// 37 INT_STA 0x00 ACC_NM ACC_AM ACC_HIGH_G GYR_DRDY GYR_HIGH_RATE GYRO_AM MAG_DRDY ACC_BSX_DRDY
#pragma pack(push, 1)
struct StatusInterrupt {
byte accel_bsx_drdy : 1;
byte mag_drdy : 1;
byte gyro_am : 1;
byte gyro_high_rate : 1;
byte gyro_drdy : 1;
byte accel_high_g : 1;
byte accel_am : 1;
byte accel_nm : 1;
};
#pragma pack(pop)
StatusInterrupt registerByte = {0};
// Read all tht INT_STA addr to get all interrupt status in one read
// after the read the register is cleared
BNO055_RETURN_FUNCTION_TYPE res = bno055_read_register(BNO055_INT_STA_ADDR, (unsigned char *)(®isterByte), 1);
if (res == 0) {
if (synthetic){
Serial.print("Anm Aam Ahg Grd Ggr Gam Mrd Abr --> ");
Serial.print( registerByte.accel_nm );
Serial.print( registerByte.accel_am );
Serial.print( registerByte.accel_high_g );
Serial.print( registerByte.gyro_drdy );
Serial.print( registerByte.gyro_high_rate );
Serial.print( registerByte.gyro_am );
Serial.print( registerByte.mag_drdy );
Serial.println( registerByte.accel_bsx_drdy );
}else{
Serial.print( "Gyro Any Motion " );
Serial.println( registerByte.gyro_am );
Serial.print( "Gyro High Rate " );
Serial.println( registerByte.gyro_high_rate );
Serial.print( "Accel High G " );
Serial.println( registerByte.accel_high_g );
Serial.print( "Accel Any Motion " );
Serial.println( registerByte.accel_am );
Serial.print( "Accel No Motion " );
Serial.println( registerByte.accel_nm );
}
} else {
Serial.println("Error status!");
}
}
void printSlowMotionNoMotionParameters(){
unsigned char accel_slow_no_thr = 0;
bno055_get_accel_slow_no_threshold(&accel_slow_no_thr);
Serial.print("Slow motion/no motion threshold: ");
Serial.println(accel_slow_no_thr);
unsigned char accel_am_dur = 0;
bno055_get_accel_anymotion_duration(&accel_am_dur);
Serial.print("Slow motion/no motion duration: ");
Serial.println(accel_am_dur);
}
Ora la stessa operazione si traduce in questo output seriale, quando si verificherà un interrupt sul pin, stampo delle informazioni più dettagliate in questo modo.
---------------
Gyro Any Motion 0
Gyro High Rate 0
Accel High G 0
Accel Any Motion 0
Accel No Motion 1
---------------
Ecco l’output completo.
Connetti alla porta seriale COM27 a 115200
---- Interrupt enabled ----
Gyro Any Motion 0
Gyro High Rate 0
Accel High G 0
Accel Any Motion 1
Accel No Motion 1
---------------------------
---- Interrupt bitmask ----
Gyro Any Motion 0
Gyro High Rate 0
Accel High G 0
Accel Any Motion 1
Accel No Motion 1
---------------------------
Slow motion/no motion threshold: 10
Slow motion/no motion duration: 3
2Secs - Orientation: 360.00, 363.00, 353.00 - Anm Aam Ahg Grd Ggr Gam Mrd Abr --> 00000000
3Secs - Orientation: 360.00, 363.00, 353.00 - Anm Aam Ahg Grd Ggr Gam Mrd Abr --> 00000000
4Secs - Orientation: 359.62, 363.00, 353.00 - Anm Aam Ahg Grd Ggr Gam Mrd Abr --> 00000000
---------------
Gyro Any Motion 0
Gyro High Rate 0
Accel High G 0
Accel Any Motion 1
Accel No Motion 0
---------------
5Secs - Orientation: 358.00, 362.94, 353.00 - Anm Aam Ahg Grd Ggr Gam Mrd Abr --> 00000000
---------------
Gyro Any Motion 0
Gyro High Rate 0
Accel High G 0
Accel Any Motion 1
Accel No Motion 0
---------------
6Secs - Orientation: 358.37, 362.56, 353.25 - Anm Aam Ahg Grd Ggr Gam Mrd Abr --> 00000000
---------------
Gyro Any Motion 0
Gyro High Rate 0
Accel High G 0
Accel Any Motion 1
Accel No Motion 0
---------------
7Secs - Orientation: 357.25, 363.06, 352.87 - Anm Aam Ahg Grd Ggr Gam Mrd Abr --> 00000000
8Secs - Orientation: 357.25, 363.06, 352.87 - Anm Aam Ahg Grd Ggr Gam Mrd Abr --> 00000000
9Secs - Orientation: 357.25, 363.06, 352.87 - Anm Aam Ahg Grd Ggr Gam Mrd Abr --> 00000000
10Secs - Orientation: 357.25, 363.06, 352.87 - Anm Aam Ahg Grd Ggr Gam Mrd Abr --> 00000000
11Secs - Orientation: 357.25, 363.06, 352.87 - Anm Aam Ahg Grd Ggr Gam Mrd Abr --> 00000000
12Secs - Orientation: 357.25, 363.06, 352.87 - Anm Aam Ahg Grd Ggr Gam Mrd Abr --> 00000000
---------------
Gyro Any Motion 0
Gyro High Rate 0
Accel High G 0
Accel Any Motion 0
Accel No Motion 1
---------------
13Secs - Orientation: 357.25, 363.06, 352.87 - Anm Aam Ahg Grd Ggr Gam Mrd Abr --> 00000000
14Secs - Orientation: 357.25, 363.06, 352.87 - Anm Aam Ahg Grd Ggr Gam Mrd Abr --> 00000000
15Secs - Orientation: 357.25, 363.06, 352.87 - Anm Aam Ahg Grd Ggr Gam Mrd Abr --> 00000000
È inoltre possibile gestire eventuali interruzioni di movimento per un singolo asse disabilitando gli altri.
// Disable anymotion on X axis
bno055_set_accel_an_nm_axis_enable(BNO055_ACCEL_AM_NM_X_AXIS, 0);
// Enable anymotion on Y axis
bno055_set_accel_an_nm_axis_enable(BNO055_ACCEL_AM_NM_Y_AXIS, 1);
Come per gli altri parametri, puoi recuperare il valore per l’asse.
unsigned char xEnabled = 0;
bno055_get_accel_an_nm_axis_enable(BNO055_ACCEL_AM_NM_X_AXIS, &xEnabled);
Accelerometro High G Interrupt
Questa interruzione si basa sul confronto dei dati di accelerazione rispetto a una soglia g per il rilevamento di urti o altri eventi di accelerazione elevata.
| Params | Value |
|---|---|
| Interrupt Parameters | Threshold |
| Duration | |
| Axis selection | X-axis |
| Y-axis | |
| Z-axis |
L’interrupt high-g è abilitato (disabilitato) per asse. Di default tutti gli assi sono disabilitati . È possibile impostare la soglia high-g.
// Disable high g on X axis
bno055_set_accel_high_g_axis_enable(BNO055_ACCEL_HIGH_G_X_AXIS, 0);
// Enable high g on Y axis
bno055_set_accel_high_g_axis_enable(BNO055_ACCEL_HIGH_G_Y_AXIS, 1);
E l’operazione inversa per recuperare valore.
unsigned char xEnabled = 0;
bno055_get_accel_high_g_axis_enable(BNO055_ACCEL_HIGH_G_X_AXIS, &xEnabled);
L’interrupt high-g viene generato se il valore assoluto dell’accelerazione di almeno uno degli assi abilitati (relazione ´or´) è superiore alla soglia per almeno il tempo definito dalla durata di high-g.
Per impostare la durata, puoi usare questo comando.
bno055_set_accel_high_g_duration(15);
Dove il parametro è un puntatore ACC_HG_DURATION e puoi calcolare i millisecondi di ritardo con [ms] = [ACC_HG_DURATION + 1] * 2 ms, il valore massimo in millisecondi è 512 (valore del puntatore a 7 bit).
La soglia high-g dipendeva dall’intervallo g configurato, corrispondente a 7,81 mg nell’intervallo 2g, 15,63 mg nell’intervallo 4g, 31,25 mg nell’intervallo 8g e 62,5 mg nell’intervallo 16g (ovvero l’incremento dipende dall’intervallo g collocamento). Per impostare la soglia, puoi usare questo comando.
bno055_set_accel_high_g_threshold(192);
L’interrupt viene resettato se il valore assoluto dell’accelerazione di tutti gli assi abilitati (relazione ´e´) è inferiore alla soglia per almeno il tempo definito dalla durata high-g. Pertanto, i possibili tempi di ritardo vanno da 2 ms a 512 ms.
Qui uno sketch completo.
/**
* bno055 simple interrupt management
* enable register interrupt and pin 15
* for high-g acceleration
* bit mask for interrupt pin on high-g acceleration
*
* by Renzo Mischianti <www.mischianti.org>
*
* https://mischianti.org/
*/
#include "BNO055_support.h" //Contains the bridge code between the API and Arduino
#include <Wire.h>
//The device address is set to BNO055_I2C_ADDR2 in this example. You can change this in the BNO055.h file in the code segment shown below.
// /* bno055 I2C Address */
// #define BNO055_I2C_ADDR1 0x28
// #define BNO055_I2C_ADDR2 0x29
// #define BNO055_I2C_ADDR BNO055_I2C_ADDR2
//Pin assignments as tested on the Arduino Due.
//Vdd,Vddio : 3.3V
//GND : GND
//SDA/SCL : SDA/SCL
//PSO/PS1 : GND/GND (I2C mode)
//This structure contains the details of the BNO055 device that is connected. (Updated after initialization)
struct bno055_t myBNO;
struct bno055_euler myEulerData; //Structure to hold the Euler data
unsigned long lastTime = 0;
/* Set the delay between fresh samples */
#define BNO055_SAMPLERATE_DELAY_MS (1000)
#define INTERRUPT_PIN 15
void getIntInterruptEnabled();
void getIntInterruptBitMaskEnabled();
void getInterruptStatusEnabled(bool synthetic = false);
void printAccelHighGParameters();
bool somethingHappened = false;
void IRAM_ATTR interruptCallback() {
somethingHappened = true;
}
void setup() //This code is executed once
{
//Initialize I2C communication
Wire.begin();
//Initialization of the BNO055
BNO_Init(&myBNO); //Assigning the structure to hold information about the device
// bno055_set_reset_sys(1);
delay(1500);
bno055_set_powermode(POWER_MODE_NORMAL);
// disable nomotion and anymotion
bno055_set_int_accel_anymotion(0);
bno055_set_int_accel_nomotion(0);
// Activate INT pin with bitmask
bno055_set_intmsk_accel_nomotion(0);
bno055_set_intmsk_accel_anymotion(0);
// Activate acceleration high-g and bit mask fot INT pin
bno055_set_int_accel_high_g(1);
bno055_set_intmsk_accel_high_g(1);
// bno055_set_accel_high_g_threshold(192);
// bno055_set_accel_high_g_duration(15);
bno055_set_accel_high_g_axis_enable(BNO055_ACCEL_HIGH_G_X_AXIS, 1);
bno055_set_accel_high_g_axis_enable(BNO055_ACCEL_HIGH_G_Y_AXIS, 1);
bno055_set_accel_high_g_axis_enable(BNO055_ACCEL_HIGH_G_Z_AXIS, 1);
// reset all previous int signal
bno055_set_reset_int(1);
//Configuration to NDoF mode
bno055_set_operation_mode(OPERATION_MODE_NDOF);
delay(1);
//Initialize the Serial Port to view information on the Serial Monitor
Serial.begin(115200);
pinMode(INTERRUPT_PIN, INPUT);
attachInterrupt(INTERRUPT_PIN, interruptCallback, RISING);
delay(1000);
getIntInterruptEnabled();
getIntInterruptBitMaskEnabled();
printAccelHighGParameters();
}
bool suspended = false;
bool reactivated = false;
void loop() //This code is looped forever
{
if ((millis() - lastTime) >= BNO055_SAMPLERATE_DELAY_MS) //To stream at 10Hz without using additional timers
{
lastTime = millis();
bno055_read_euler_hrp(&myEulerData); //Update Euler data into the structure
Serial.print(millis()/1000); Serial.print("Secs - ");
/* The WebSerial 3D Model Viewer expects data as heading, pitch, roll */
Serial.print(F("Orientation: "));
Serial.print(360-(float(myEulerData.h) / 16.00));
Serial.print(F(", "));
Serial.print(360-(float(myEulerData.p) / 16.00));
Serial.print(F(", "));
Serial.print(360-(float(myEulerData.r) / 16.00));
Serial.print(F(" - "));
getInterruptStatusEnabled(true);
}
if (somethingHappened) {
Serial.println("---------------");
getInterruptStatusEnabled();
Serial.println("---------------");
bno055_set_reset_int(1);
somethingHappened = false;
}
}
/*
* Print the interrupt enabled
*/
void getIntInterruptEnabled() {
unsigned char gyro_am = 0;
unsigned char gyro_hr = 0;
unsigned char accel_hg = 0;
unsigned char accel_am = 0;
unsigned char accel_nm = 0;
bno055_get_int_gyro_anymotion(&gyro_am);
bno055_get_int_gyro_highrate(&gyro_hr);
bno055_get_int_accel_high_g(&accel_hg);
bno055_get_int_accel_anymotion(&accel_am);
bno055_get_int_accel_nomotion(&accel_nm);
Serial.println( "---- Interrupt enabled ----" );
Serial.print( "Gyro Any Motion " );
Serial.println( gyro_am );
Serial.print( "Gyro High Rate " );
Serial.println( gyro_hr );
Serial.print( "Accel High G " );
Serial.println( accel_hg );
Serial.print( "Accel Any Motion " );
Serial.println( accel_am );
Serial.print( "Accel No Motion " );
Serial.println( accel_nm );
Serial.println( "---------------------------" );
}
/*
* Print the interrupt to send on interrupt pin
*/
void getIntInterruptBitMaskEnabled() {
unsigned char gyro_am = 0;
unsigned char gyro_hr = 0;
unsigned char accel_hg = 0;
unsigned char accel_am = 0;
unsigned char accel_nm = 0;
bno055_get_intmsk_gyro_anymotion(&gyro_am);
bno055_get_intmsk_gyro_highrate(&gyro_hr);
bno055_get_intmsk_accel_high_g(&accel_hg);
bno055_get_intmsk_accel_anymotion(&accel_am);
bno055_get_intmsk_accel_nomotion(&accel_nm);
Serial.println( "---- Interrupt bitmask ----" );
Serial.print( "Gyro Any Motion " );
Serial.println( gyro_am );
Serial.print( "Gyro High Rate " );
Serial.println( gyro_hr );
Serial.print( "Accel High G " );
Serial.println( accel_hg );
Serial.print( "Accel Any Motion " );
Serial.println( accel_am );
Serial.print( "Accel No Motion " );
Serial.println( accel_nm );
Serial.println( "---------------------------" );
}
/*
* Print the interrupt status
*/
void getInterruptStatusEnabled(bool synthetic) {
// 37 INT_STA 0x00 ACC_NM ACC_AM ACC_HIGH_G GYR_DRDY GYR_HIGH_RATE GYRO_AM MAG_DRDY ACC_BSX_DRDY
#pragma pack(push, 1)
struct StatusInterrupt {
byte accel_bsx_drdy : 1;
byte mag_drdy : 1;
byte gyro_am : 1;
byte gyro_high_rate : 1;
byte gyro_drdy : 1;
byte accel_high_g : 1;
byte accel_am : 1;
byte accel_nm : 1;
};
#pragma pack(pop)
StatusInterrupt registerByte = {0};
// Read all tht INT_STA addr to get all interrupt status in one read
// after the read the register is cleared
BNO055_RETURN_FUNCTION_TYPE res = bno055_read_register(BNO055_INT_STA_ADDR, (unsigned char *)(®isterByte), 1);
if (res == 0) {
if (synthetic){
Serial.print("Anm Aam Ahg Grd Ggr Gam Mrd Abr --> ");
Serial.print( registerByte.accel_nm );
Serial.print( registerByte.accel_am );
Serial.print( registerByte.accel_high_g );
Serial.print( registerByte.gyro_drdy );
Serial.print( registerByte.gyro_high_rate );
Serial.print( registerByte.gyro_am );
Serial.print( registerByte.mag_drdy );
Serial.println( registerByte.accel_bsx_drdy );
}else{
Serial.print( "Gyro Any Motion " );
Serial.println( registerByte.gyro_am );
Serial.print( "Gyro High Rate " );
Serial.println( registerByte.gyro_high_rate );
Serial.print( "Accel High G " );
Serial.println( registerByte.accel_high_g );
Serial.print( "Accel Any Motion " );
Serial.println( registerByte.accel_am );
Serial.print( "Accel No Motion " );
Serial.println( registerByte.accel_nm );
}
} else {
Serial.println("Error status!");
}
}
void printAccelHighGParameters(){
unsigned char accel_hg_dur = 0;
bno055_get_accel_high_g_duration(&accel_hg_dur);
Serial.print("Accel high-g duration: ");
Serial.println(accel_hg_dur);
unsigned char accel_hg_thr = 0;
bno055_get_accel_high_g_threshold(&accel_hg_thr);
Serial.print("Accel high-g threshold: ");
Serial.println(accel_hg_thr);
unsigned char xEnabled = 0;
bno055_get_accel_high_g_axis_enable(BNO055_ACCEL_HIGH_G_X_AXIS, &xEnabled);
Serial.print("X axis high-g enabled: ");
Serial.println(xEnabled);
unsigned char yEnabled = 0;
bno055_get_accel_high_g_axis_enable(BNO055_ACCEL_HIGH_G_Y_AXIS, &yEnabled);
Serial.print("Y axis high-g enabled: ");
Serial.println(yEnabled);
unsigned char zEnabled = 0;
bno055_get_accel_high_g_axis_enable(BNO055_ACCEL_HIGH_G_Z_AXIS, &zEnabled);
Serial.print("Z axis high-g enabled: ");
Serial.println(zEnabled);
}
Il risultato nell’output seriale è questo.
---- Interrupt enabled ----
Gyro Any Motion 0
Gyro High Rate 0
Accel High G 1
Accel Any Motion 0
Accel No Motion 0
---------------------------
---- Interrupt bitmask ----
Gyro Any Motion 0
Gyro High Rate 0
Accel High G 1
Accel Any Motion 0
Accel No Motion 0
---------------------------
Accel high-g duration: 15
Accel high-g threshold: 192
X axis high-g enabled: 1
Y axis high-g enabled: 1
Z axis high-g enabled: 1
2Secs - Orientation: 85.25, 363.37, 357.00 - Anm Aam Ahg Grd Ggr Gam Mrd Abr --> 00000000
3Secs - Orientation: 90.00, 358.37, 355.62 - Anm Aam Ahg Grd Ggr Gam Mrd Abr --> 00000000
---------------
Gyro Any Motion 0
Gyro High Rate 0
Accel High G 1
Accel Any Motion 0
Accel No Motion 0
---------------
4Secs - Orientation: 94.19, 329.00, 368.44 - Anm Aam Ahg Grd Ggr Gam Mrd Abr --> 00000000
---------------
Gyro Any Motion 0
Gyro High Rate 0
Accel High G 1
Accel Any Motion 0
Accel No Motion 0
---------------
5Secs - Orientation: 92.75, 341.56, 367.75 - Anm Aam Ahg Grd Ggr Gam Mrd Abr --> 00000000
6Secs - Orientation: 86.69, 365.50, 360.56 - Anm Aam Ahg Grd Ggr Gam Mrd Abr --> 00000000
7Secs - Orientation: 87.31, 364.56, 360.31 - Anm Aam Ahg Grd Ggr Gam Mrd Abr --> 00000000
Puoi vedere evidenziato l’output quando scuoto il sensore.
Grazie
- BNO055 accelerometro, giroscopio, magnetometro con la semplice libreria Adafruit
- BNO055 per esp32, esp8266 e Arduino: cablaggio e libreria Bosch avanzata
- BNO055 per esp32, esp8266 e Arduino: caratteristiche, configurazione e rimappatura assi
- BNO055: modalità di alimentazione, accelerometro e interrupt di movimento
- BNO055 per esp32, esp8266 e Arduino: abilitare il pin INT e High G Interrupt dell’accelerometro
- BNO055 per esp32, esp8266 e Arduino: giroscopio ad alta velocità e interrupt per ogni movimento