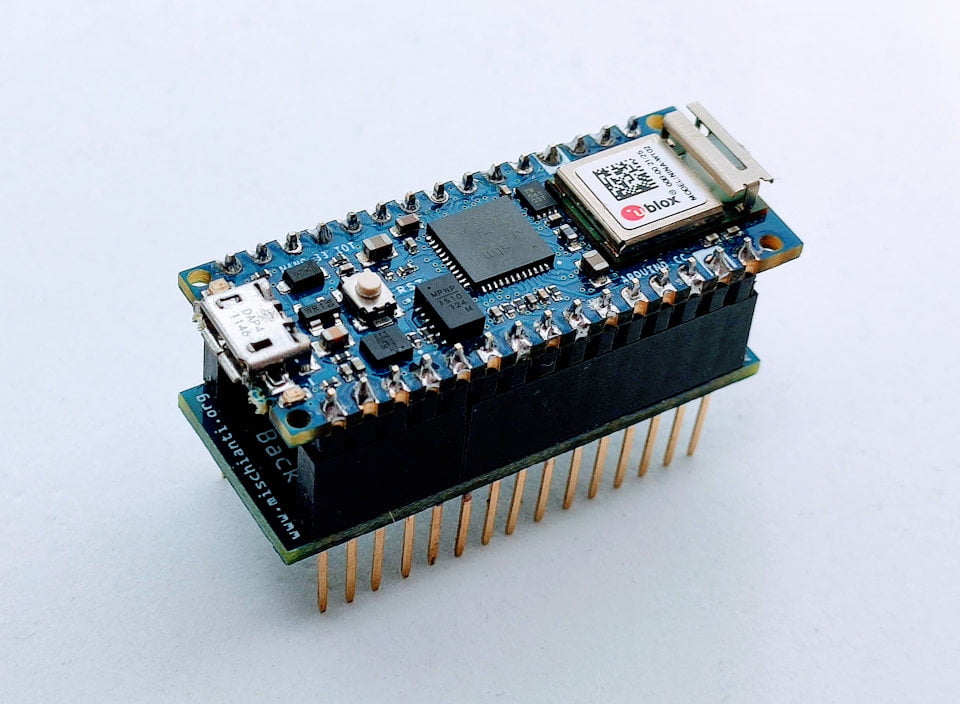
Arduino NANO 33 IoT SPI Flash memory shield
Like the Arduino MKR WiFi 1010, the NANO 33 IoT doesn’t have Flash memory to store data. I wrote an article that explains how to interface these kinds of memory, “How to use external SPI Flash memories“, and I’d like to simplify the process of adding these chips, so I created another simple PCB shield to add external SPI Flash memory in the fastest way.

PCB
Here the PCB shield PCBWay

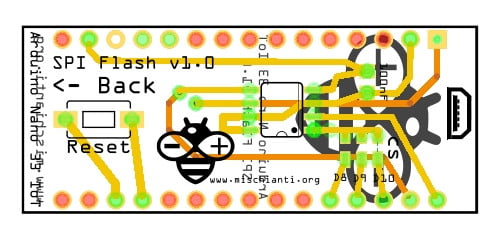
The PCB is quite simple, and I’ve added some solder jumpers to select the CS pin.
The configuration is the same as the examples already posted.
Pay attention to CS pin that is selectable.
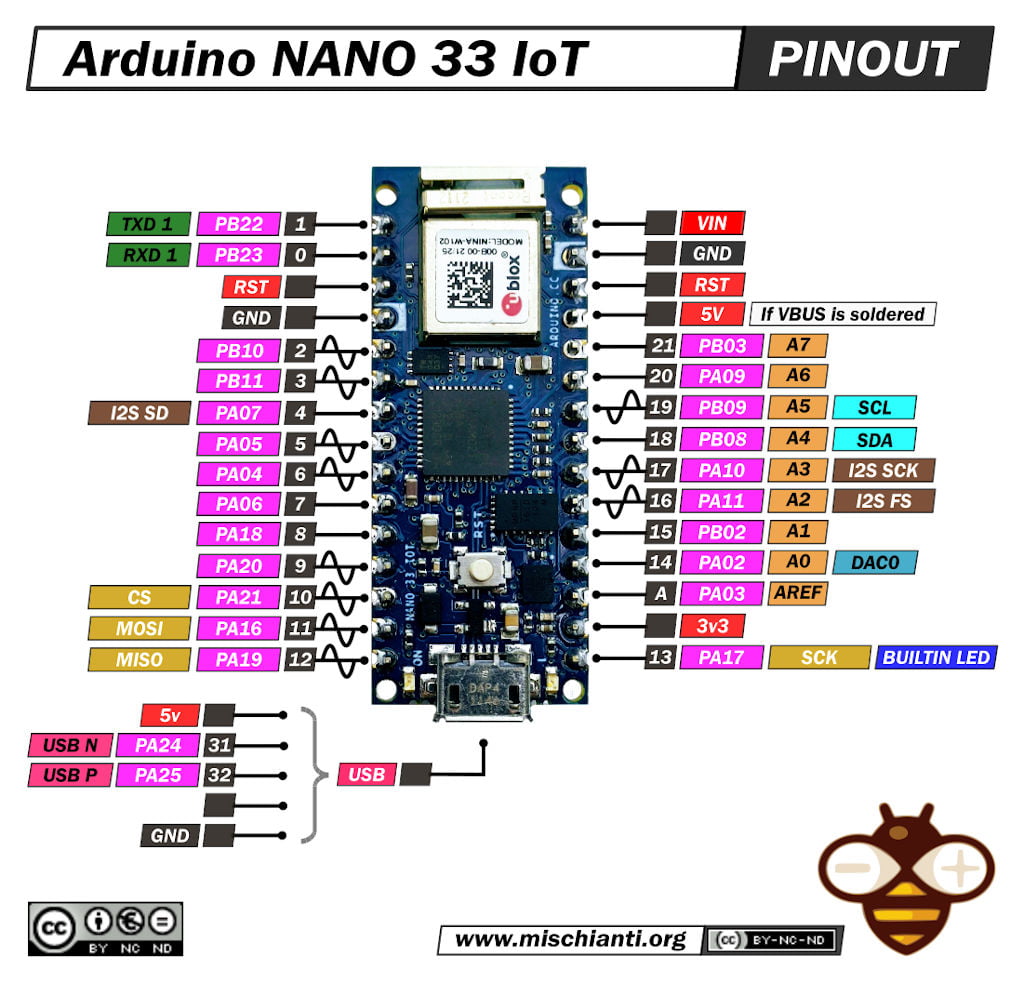
| Arduino | SPI Flash | |
|---|---|---|
| 10 | /CS | Pulled UP if not standard CS |
| 12 | DI (IO1) | |
| 11 | DI (IO0) | |
| 13 | CLK | |
| 3.3v | /WP | |
| 3.3v | /Hold | |
| GND | GND | |
| 3.3v | VCC |
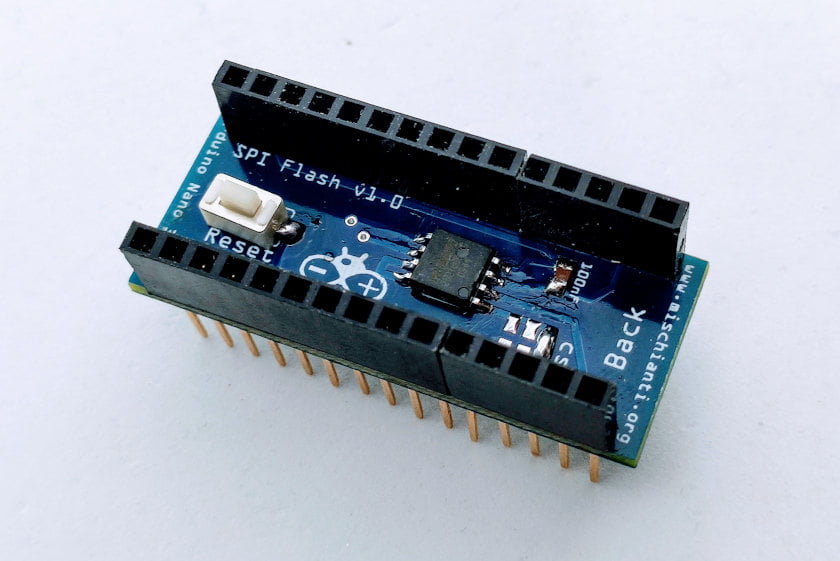
From the up, you can see how the shield appears.
For my purpose, I usually use an 8Mb Flash w25q64 chip which is sufficient for almost anything.
Here my SPI Flash selection w25q16 SMD 2Mb - w25q16 Discrete 2Mb - w25q32 SMD 4Mb - w25q32 Discrete 4Mb - w25q64 SMD 8Mb - w25q64 Discrete 8Mb - w25q128 SMD 16Mb - w25q128 Discrete 16Mb W25Q32 W25Q64 w25q128 module 4Mb 8Mb 16Mb
Here the SMD buttons 3*6*2.5 SMD buttons 3X6X2.5
SMD 805 capacitory 0805 SMD Capacitor kit
The result Is very useful, and the space used Is limited.
Example Sketch
Here is a simple example.
/*
* Use SPIFlash with FAT filesystem
* Write data inside a file
* Read data and info from the file
* Get the list of files in the directory
*
* library Adafruit_SPIFlash and SdFat - AdafruitFork
*
* by Mischianti Renzo <https://mischianti.org>
*
* https://mischianti.org/
*
* SPIFlash connected via SPI standard check wiring on the article
*
*/
#include "SdFat.h"
#include "Adafruit_SPIFlash.h"
Adafruit_FlashTransport_SPI flashTransport(SS, SPI); // Set CS and SPI interface
Adafruit_SPIFlash flash(&flashTransport);
// file system object from SdFat
FatFileSystem fatfs;
//The setup function is called once at startup of the sketch
void setup()
{
// Initialize serial port and wait for it to open before continuing.
Serial.begin(115200);
while (!Serial) {
delay(100);
}
Serial.println("Adafruit SPI Flash FatFs Full Usage Example");
// Initialize flash library and check its chip ID.
if (!flash.begin()) {
Serial.println("Error, failed to initialize flash chip!");
while(1) yield();
}
Serial.print("JEDEC ID: "); Serial.println(flash.getJEDECID(), HEX);
Serial.print("Flash size: "); Serial.println(flash.size());
Serial.flush();
// First call begin to mount the filesystem. Check that it returns true
// to make sure the filesystem was mounted.
if (!fatfs.begin(&flash)) {
Serial.println("Error, failed to mount newly formatted filesystem!");
Serial.println("Was the flash chip formatted with the SdFat_format example?");
while(1) yield();
}
Serial.println("Mounted filesystem!");
Serial.println();
// create directory mischianti if not exist
if (!fatfs.exists("/mischianti")) {
Serial.println("mischianti directory not found, creating...");
// Use mkdir to create directory (note you should _not_ have a trailing slash).
fatfs.mkdir("/mischianti");
if ( !fatfs.exists("/mischianti") ) {
Serial.println("Error, failed to create directory!");
while(1) yield();
}else {
Serial.println("Created directory!");
}
}
Serial.println();
// Create a file
File writeFile = fatfs.open("/test.txt", FILE_WRITE);
if (writeFile) {
Serial.println("Opened file /test.txt for writing/appending...");
// Once open for writing you can print to the file as if you're printing
// to the serial terminal, the same functions are available.
writeFile.println("www.mischianti.org");
writeFile.print("Write a number: "); writeFile.println(123, DEC);
writeFile.print("Write HEX number: 0x"); writeFile.println(123, HEX);
// Close the file when finished writing.
writeFile.close();
Serial.println("Wrote to file /test.txt!");
} else {
Serial.println("Error, failed to open test.txt for writing!");
while(1) yield();
}
Serial.println();
// Now open the same file but for reading.
File readFile = fatfs.open("/test.txt", FILE_READ);
if (readFile) {
// Read a line of data:
String line = readFile.readStringUntil('\n');
Serial.print("First line of test.txt: "); Serial.println(line);
// You can get the current position, remaining data, and total size of the file:
Serial.print("Total size of test.txt (bytes): "); Serial.println(readFile.size(), DEC);
Serial.print("Current position in test.txt: "); Serial.println(readFile.position(), DEC);
Serial.print("Available data to read in test.txt: "); Serial.println(readFile.available(), DEC);
char filename[64];
readFile.getName(filename, sizeof(filename));
Serial.print("File name: "); Serial.println(filename);
Serial.print("Is file a directory? "); Serial.println(readFile.isDirectory() ? "Yes" : "No");
} else {
Serial.println("Error, failed to open test.txt for reading!");
while(1) yield();
}
Serial.println();
// You can open a directory to list all the children (files and directories).
File testDir = fatfs.open("/");
if (testDir) {
if (!testDir.isDirectory()) {
Serial.println("Error, expected test to be a directory!");
while(1) yield();
}
Serial.println("Listing children of directory /:");
File child = testDir.openNextFile();
while (child) {
Serial.print(child.size()); Serial.print("bytes \t");
char filename[64];
child.getName(filename, sizeof(filename));
// Print the file name and mention if it's a directory.
Serial.print("- "); Serial.print(filename);
if (child.isDirectory()) {
Serial.print(" (directory)");
}
Serial.println();
// Keep calling openNextFile to get a new file.
child = testDir.openNextFile();
}
Serial.println();
Serial.println("All file in the directory writed");
} else {
Serial.println("Error, failed to open test directory!");
while(1) yield();
}
}
// The loop function is called in an endless loop
void loop()
{
}
And here is the Serial output.
Connetti alla porta seriale COM19 a 115200
Adafruit SPI Flash FatFs Full Usage Example
JEDEC ID: EF4017
Flash size: 8388608
Mounted filesystem!
mischianti directory not found, creating...
Created directory!
Opened file /test.txt for writing/appending...
Wrote to file /test.txt!
First line of test.txt: www.mischianti.org
Total size of test.txt (bytes): 65
Current position in test.txt: 20
Available data to read in test.txt: 45
File name: test.txt
Is file a directory? No
Listing children of directory /:
0bytes - mischianti (directory)
65bytes - test.txt
All file in the directory writed
Thanks
- Arduino SAMD NINA: pinout, specs and Arduino IDE configuration
- Arduino SAMD NINA: WiFiNINA, firmware update, and RGB led
- Arduino SAMD (NANO 33 and MKR): SPI flash memory FAT FS
- i2c Arduino SAMD MKR: additional interface SERCOM, network and address scanner
- Arduino MKR SAMD: FAT filesystem on external SPI flash memory
- Connecting the EByte E70 to Arduino SAMD (Nano 33, MKR…) devices and a simple sketch example