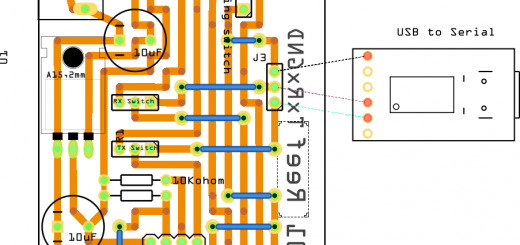
How to Send Emails with Attachments on ESP32/ESP8266 (EMailSender v4.0.0 & STARTTLS)
And finally, the updated guide for using EMailSender v4.0.0 on ESP32 and ESP8266! This tutorial covers everything you need to know about sending secure emails from your ESP32 board using the new STARTTLS support on port 587.