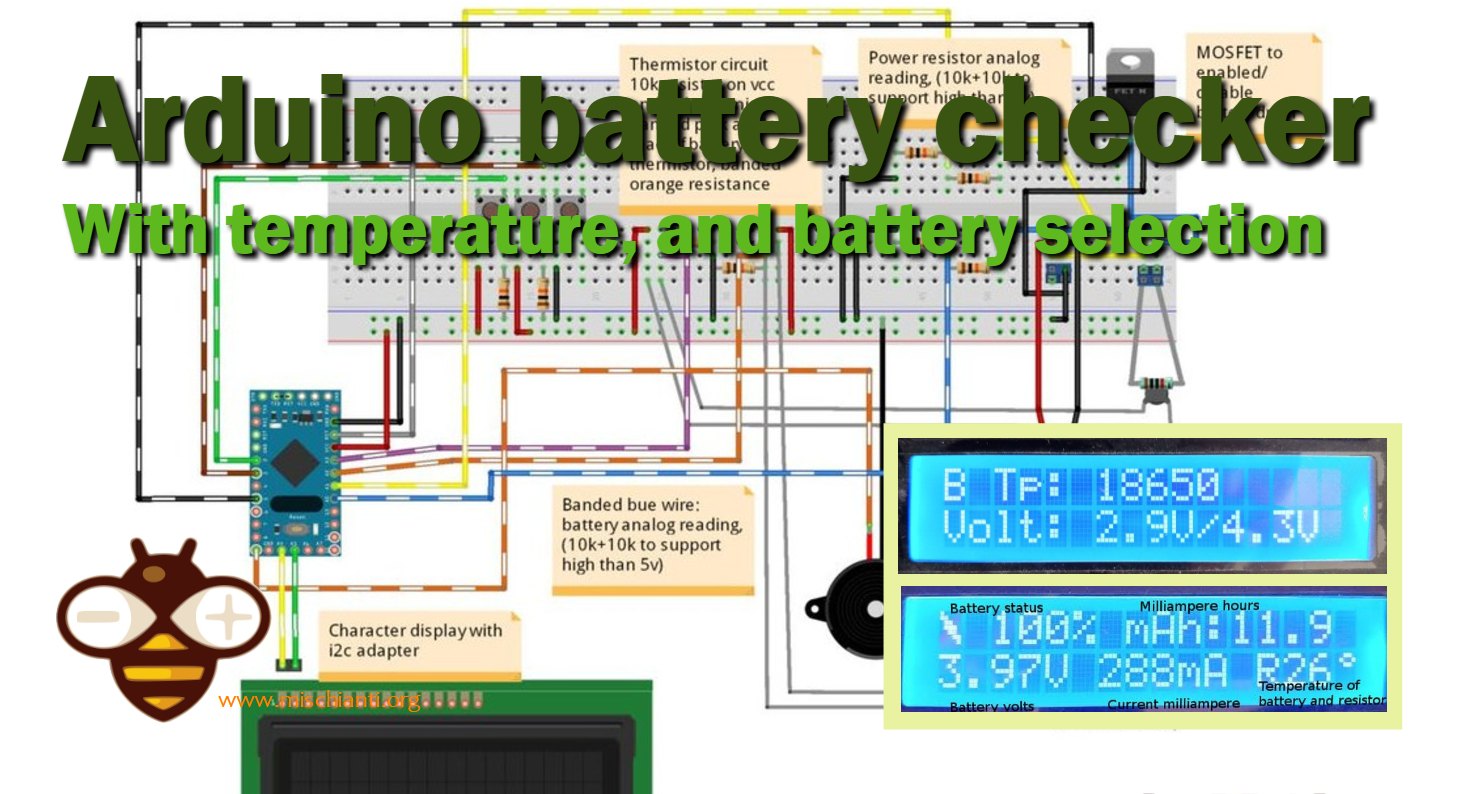
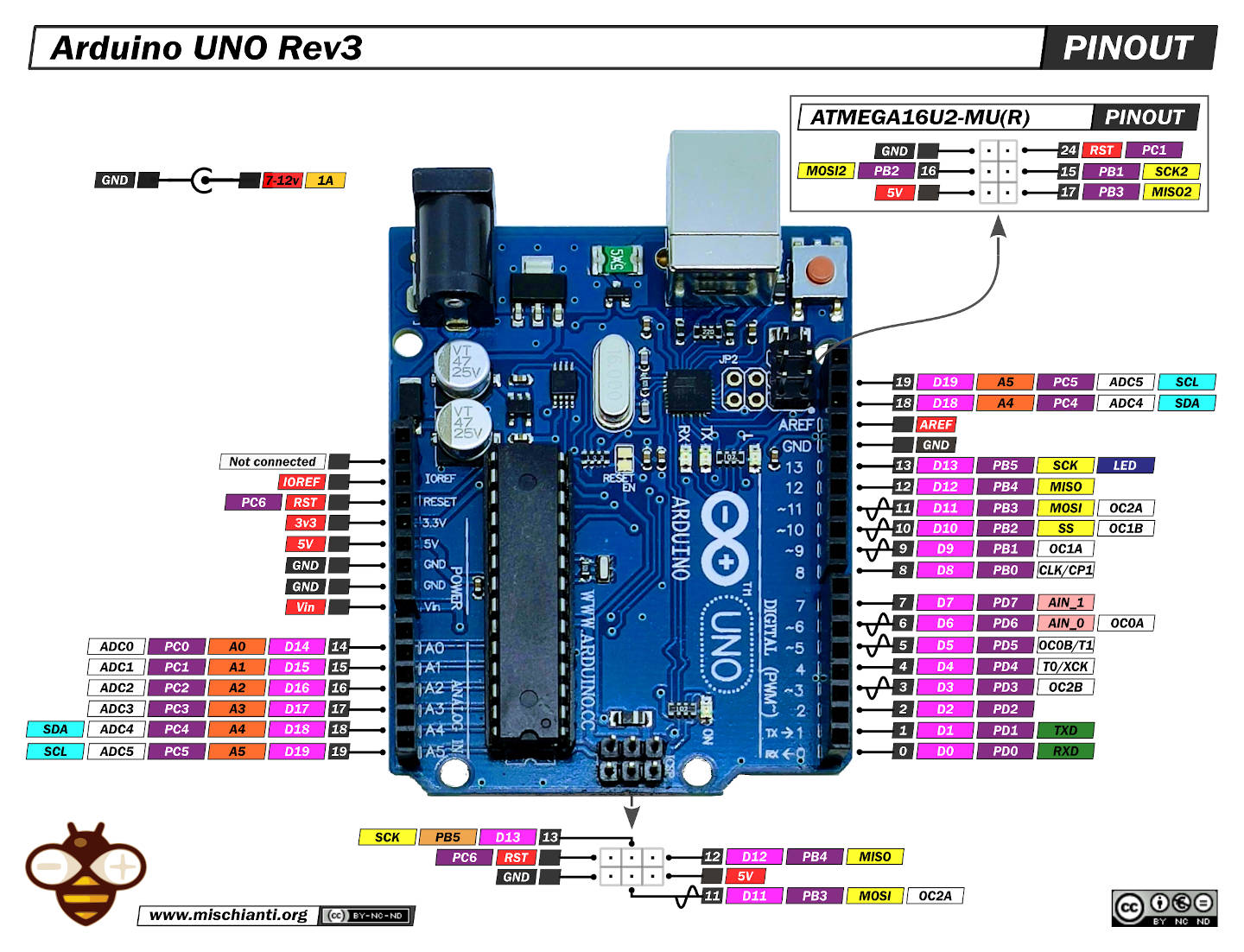
Checking Battery Capacity with Arduino: Temperature Monitoring and Type Selection
Here is my Arduino battery tester, designed to explore the performance of various types of batteries, including 18650 and acid-based ones. Successfully tested even with a 6V lead-acid battery with a capacity of 4.2A, this device provides battery capacity readings in milliampere-hours. In fact, it’s an old article that I had never published before, but I have revisited and decided to publish it now.